Streamlining Business Processes with EDI Optimization
Unlocking Efficiency: How EDI Streamlines Business Operations

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the importance of efficient data exchange cannot be overstated. Regardless of the industry, accurate and timely data transfer is crucial for businesses to maintain seamless operations, make informed decisions, and stay competitive. Errors and delays in data exchange can lead to costly disruptions, miscommunications, and missed opportunities.
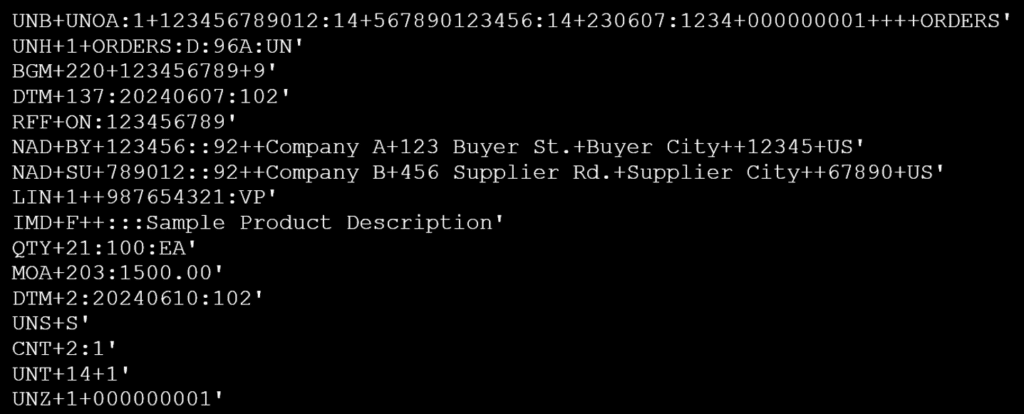
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a file format that enables the standardized electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in commerce using multi structured delimited files [1]. EDI is extensively used across various industries. In retail, it manages purchase orders, invoices, and inventory updates between retailers and suppliers. In manufacturing, EDI coordinates supply chain activities such as order processing, shipping notifications, and invoicing. The healthcare industry uses EDI to exchange patient records, insurance claims, and payment information between healthcare providers and insurers. In logistics, EDI facilitates shipment scheduling, tracking, and delivery confirmation, ensuring smooth and efficient operations. Mainly, EDI facilitates business communications, including purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other critical transactions without the need for manual intervention. This automation streamlines operations, reduces errors, and accelerates the supply chain processes. At the same time, EDI operates on agreed-upon standards that define the format and structure of electronic documents. The EDI formats are periodically by the respective organizations.
An EDI message is composed of segments, which are groups of related data elements. Each data element represents a specific piece of information, such as a product price or quantity, ensuring all necessary details are included in the exchange.
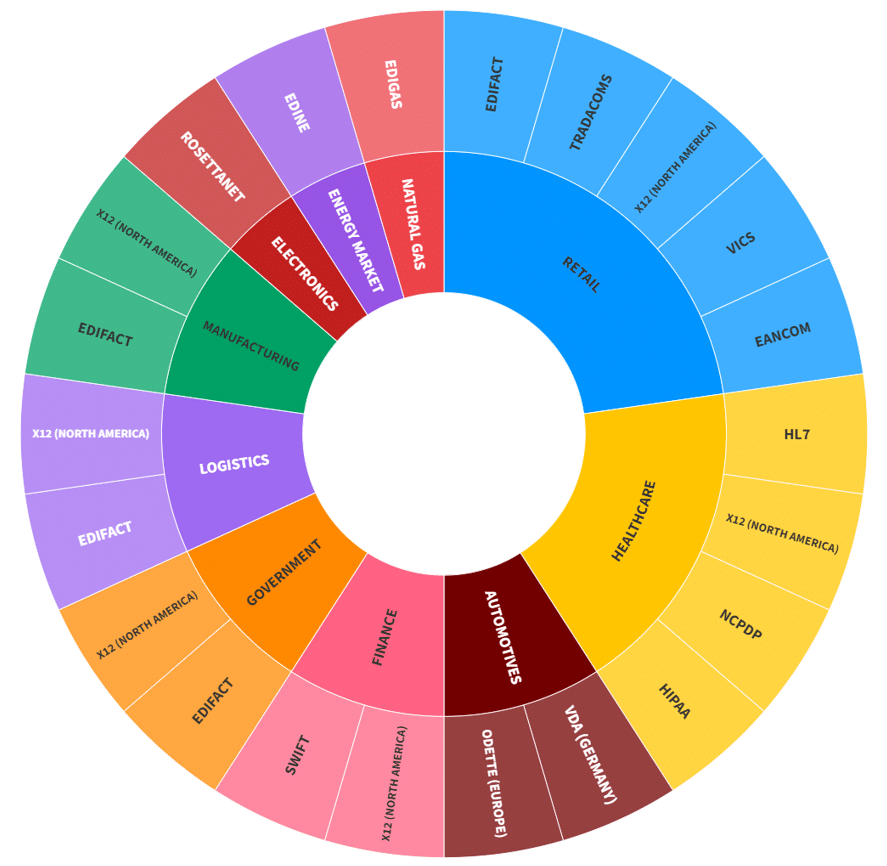
At the same time, in the present context, to ease the process of communication between the entities, there are numerous EDI standard formats are specified and generalized by the regulatory authorities [2]. Some of the common standards include SWIFT, used by banks and in the financial sector, and EDIFACT, which is utilized internationally across multiple industries. The EDI standards ensure consistency and compatibility across different systems and industries. Further, based on industry type and requirements, numerous EDI formats are available, such as HL7 in health care, ODETTE in automotives, EDINE in energy market etc. To give a better idea of the EDI formats and their usage, the details are summarized in figure 2 and table.
Figure 2: EDI standards by industry
Benefits of EDI
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) offers a multitude of benefits for businesses, streamlining operations and strengthening relationships with trading partners. Here’s a closer look at some key benefits.
- Higher Efficiency: EDI automates the entire process, seamlessly exchanging information between your systems and your trading partners. This translates to faster transactions. Orders are placed and confirmed electronically, eliminating delays and back-and-forth communication. Fewer errors also means less time spent on corrections and troubleshooting. With streamlined processes, the data is transferred with much ease and enhancing the overall system efficiency.
- Enhanced Accuracy: EDI minimizes the risk by automating data exchange. Since data is transferred electronically in a pre-defined format, the chances of errors are significantly reduced. Standardized formats ensure that the data exchanged between partners is consistent and accurate. This as a whole results in in improved data accuracy with EDI and increases the reliability of the data for much better decision making.
- Increased Speed: With a clear standard format, the transactions are faster with EDI and eliminates the delays caused by the traditional way of communication. Further EDIs ensures for quicker responses to customer and partner needs. This translates into faster order fulfillment, improved on-time deliveries.
- Stronger Trading Partner Relationships: Given the streamlined data exchange with EDI, real information is flowing with ease, enables all the partners for a better communication among their systems. Further, EDI ensures everyone is on the same page with real-time information, leading to smoother collaboration and stronger overall relationships. Additionally, faster and more accurate data exchange builds trust and strengthens your reputation as a reliable business partner.
- Standardized Communication: The standardization of EDIs enables them to serve as a universal language for businesses. At the same time, the format facilitates consistency and streamlined business processes across systems, regardless of the specific software used by various trading partners. This eliminates the need for custom translations and data mappings during the interchanges and reduces the risk of errors caused by data misinterpretations.
Challenges of EDI implementation for businesses
While the EDI offers great benefits in handling data, there are certain challenges to overcome before harnessing the benefits.
- Standardization: EDI relies on standard formats for data exchange, and businesses must ensure they use the correct format for their industry and trading partners. The lack of knowledge on standardization or non-compliance with industry standards can result in errors or delays in data exchange.
- Technical Complexity: EDI implementation requires clear understating of the EDI formats and its purpose, followed by technical expertise in data mapping, communication protocols, and security. Businesses need to setup the internal resources to implement EDI.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating EDI with existing systems can be complex and require modifications to existing software and processes. There can be a need for upgrading the legacy systems for handling the EDI, which leads to additional costs.
- Partner Readiness: EDI implementation requires coordination and collaboration with trading partners, and some partners may not be ready or willing to implement EDI.
- Security: EDI requires secure communication channels to protect sensitive business data. Businesses must implement proper security measures to ensure their data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Cost: Considering the above factors, working on EDI will require investment and needs upgrades to the present business process. There can be additional costs in setting up an EDI system, possibly involving higher initial costs for software, hardware, and professional services.
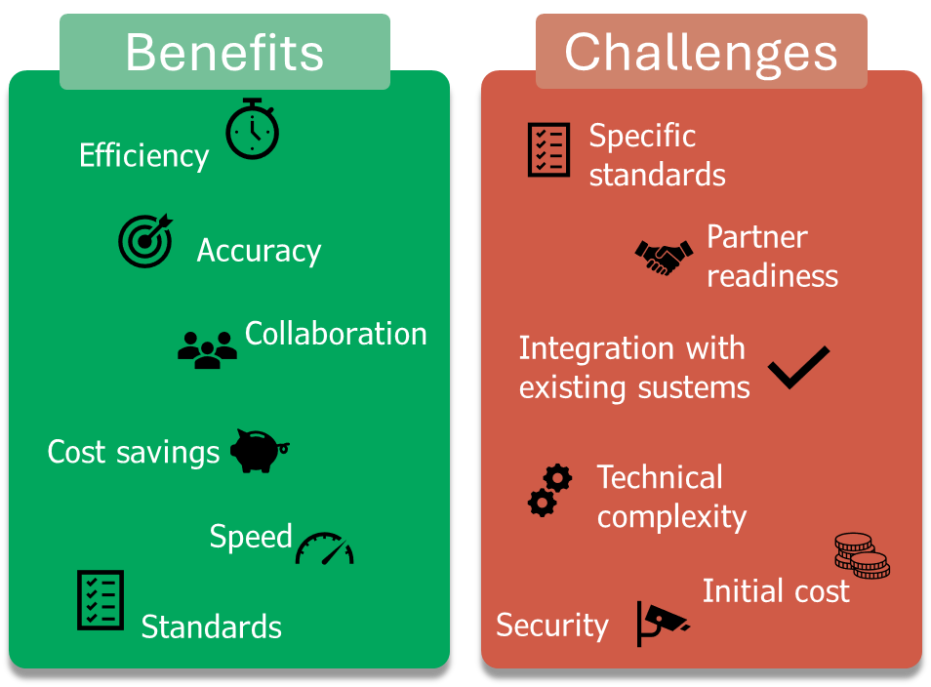
From the above discussion, it is evident that using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) offers more advantages than drawbacks. The benefits include increased efficiency, reduced errors, faster transaction processing, and cost savings by minimizing manual data entry and paperwork. However, setting up EDI messaging and effectively working with it requires a significant investment of time and resources [3]. The implementation process involves configuring the necessary software, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, adhering to industry standards, and training staff to manage and operate the EDI system. Despite the initial effort required, the long-term gains in operational efficiency and data accuracy make EDI a valuable tool for businesses aiming to streamline their data exchange processes. The benefits and challenges of using EDI are depicted in figure 3.
Figure 3: EDI benefits and challenge
Cimt’s solution in streamling EDI processes
To work with EDI and its integration across systems demands an ETL tool compatible with a wide range of EDI messaging formats. At the same time, the ETL tool should handle all the features and challenges of EDI, such as standardization, complexity, compatibility, compliance, automation, and data segmentation. Along with the ETL tool, EDI requires a good amount of skill, such as identifying the right format to ensure that data is in the correct format in line with the required standards. Similarly, maintaining high data quality is essential to ensure accuracy and reliability. Additionally, schema conversion involves converting data schemas to match required formats, and segmentation involves dividing data into manageable segments for processing. In this context, cimt recommends the Qlik Talend ETL integration solution along with their expertise in working with the EDI messaging. Given the Qlik Talend capabilities in handling the EDI messaging combined with cimt expertise ensures the businesses automate and streamline the EDI processes.
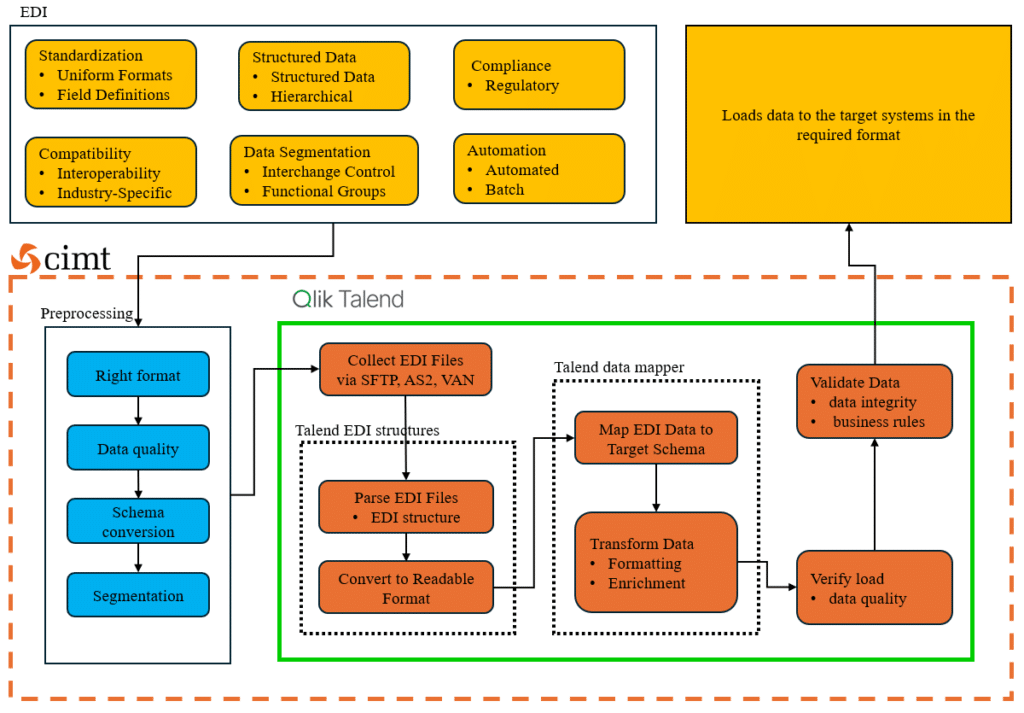
In this regard, implementing EDI using Qlik Talend ETL is a detailed process [4]. Initially EDI files are to be rightly collected from the communication partners. Qlik Talend supports numerous communications platforms for the EDI exchange with its low code components. Further, in the preprocessing stage, Qlik Talend supports most of the well-established EDI formats (i.e. X12, EDIFACT, HL7, HIPAA, etc.) in parsing the EDI files and converting them into a readable format, while maintaining the data quality in adherence to EDI standards.
In the next stage, with the help of Qlik Talend data mapper, the EDI data can be mapped to the target schema in line with the requirements. This can be converting to other data formats, transforming data, channelizing data to the targeted systems, etc. To give a better understanding of the process is shown in figure 4.
Figure 4: Methodology in handling EDI data in Qlik Talend
Conclusion
Finally, for a seamless EDI integeration, Qlik Talend offers a user-friendly solution in streamlining the EDI workflows with the trading partners for an efficient business.
Ready to overcome the challenges of EDI messaging and harness its full potential? Partner with cimt and let our expertise with Qlik and Talend tooling transform your EDI processes. Contact us today to connect with one of our consultants to analyse your situation and streamline your operations to achieve seamless electronic data interchange!
References
- Huemer, C., Liegl, P., & Zapletal, M. (2020). Electronic data interchange and standardization. Handbook of e-Tourism, 1-29.
- Buiten, G., Snijkers, G., Saraiva, P., Erikson, J., Erikson, A. G., & Born, A. (2018). Business data collection: Toward electronic data interchange. Experiences in Portugal, Canada, Sweden, and the Netherlands with EDI. Journal of Official Statistics, 34(2), 419-443.
- Tankosic, M., Dragovic, N., & Ivetic, P. (2017). Strategic communications in business success as a competitive advantage via Electronic Data Interchange. Wseas Transactions On Advances In Engineering Education, 14, 1.
- Qlik (2024). Data integration & data quality solutions. Retrieved July 5, 2024, from https://www.qlik.com/us/products/qlik-talend-data-integration-and-quality